|
ˇˇ
Brassica napus Haploid and Doubled Haploid
Production and Cloning via Combined Microspore Embryogenesis
and Somatic embryogenesis
X XuHan, H-C Jing, X-F
Cheng, A. Iwanowska, H. Keift, JHW Bergervoet, SPC Groot, RJ Bino, AAM van
Lammeren
(EU FP5 programe,
cooperation with PCB and PRI, Wageningen University, the Netherlands. Closed).
|
ˇˇ
ˇˇ
An experimental
morphogenesis research by means of cell biology, plant physiology and
biochemistry.
-
The first insight into in situ ploidy changes following development of microspore-derived embryos, plants, and secondary somatic embryos and their derived plants.
-
The first successful combination of pollen- and somatic embryogenesis, to achieve one-step cloning of
doubled haploid (DH) genotypes.
-
The first insight into in situ ploidy changes following development of microspore-derived embryos, plants, and secondary somatic embryos and their derived plants.
Main
conclusions obtained:
-
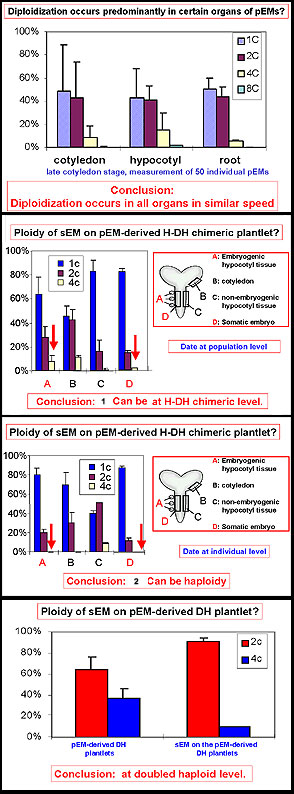
Diploidization occurs at the beginning of embryogenesis
-
Diploidization occurs in all tissues/organs if available
-
Diploidization occurs in all stages, and in similar speed
-
Diploidization leads 50% microspore embryos (pEMs) to DH or H-DH (chimerical) level
-
Ploidy doubling stops in most cases at the
DH level, does not pass tetraploidy
(TH)
-
Somatic embryos can be induced in most pEM-derived plantlets
that enables genotype cloning
-
Ploidy doubling also occurs in somatic embryogenesis
-
Somatic embryo cells at least show nuclear DNA at 1C to 8C levels
-
Similarity
of ploidy between somatic embryo (sEM) and its tissue of origin
-
Somatic embryos show an H - TH ploidy range
-
DH Somatic embryos are stabilized at DH
|
ˇˇ
ˇˇ
ˇˇ
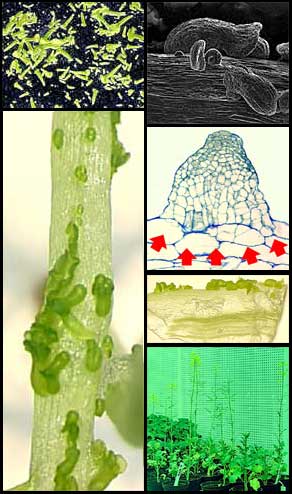
Plate 1
Morphogenesis of Brassica napus Topas
microspore embryogenesis and somatic embryogenesis.
(Photos from Protoplasma
208/240-247, 1999)
|
|
ˇˇ

Plate
2 (left) and 3 (right)
Ploidy
analyssis via flow-cytometric examinations of nuclear DNA of microspore-
and/or pollen-derived embryos (pEMs), pEM-derived plantlets, somatic embryos
(sEM), and plants.
Abbreviations:
H
= haploid DH
= doubled haploid TH
= tetraploid pEM = microspore
embryo/embryogensis sEM
= somatic embryo/embryogenesis
ˇˇ
(Figures
from Protoplasma 208/240-247, 1999)
|
|
|
ˇˇ
|
ˇˇ
ˇˇ
Related References
ˇˇ
-
Baldursson S, Ahuja MR (1996) Cytogenetics and potential of haploidy in forest tree genetics and improvement. In: Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants. Vol 1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 49 - 66
-
Binarova P, Straatman K, Hause B, Hause G, van Lammeren AAM (1993) Nuclear DNA synthesis during the induction of embryogenesis in cultured microspores and pollen of Brassica napus L. Theor Appl Genet 87: 6 - 16
-
Bino RJM, de Vries JN, Kraak HL, Van Pijlen JG (1992) Flow cytometric determination of nuclear replication stages in tomato seeds during priming and germination. Ann Bot 69: 231 ?236
-
Deverno LL (1995) An evaluation of somaclonal variation during somatic embryogenesis. In: Jain S, Gupta P, Newton R (eds) Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants. Vol 1. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 361-377
-
Ferrie AMR, Palmer CE, Keller WA (1995) Haploid embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In Vitro Embryogenesis in Plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Dordrecht. pp 309 ?344
-
Foisset N, Delourme Rm? Lucas M-O, Renard M (1997) In vitro androgenesis and segregation distortion in Brassica napus L. : spontaneous versus colchicine-doubled lines. Plant Cell Rep 16: 464 ?468
-
Gerassimova H (1936) Experimentall erhaltene haploide Pflanze von Crepis tectorum L. Planta 25: 696-702
-
Gerlach-Cruse D (1970) Experimentelle Auslösung von Semigamie bei Arabidopsis thaliana (L. ) Heynh Biol Zentralbl 89: 435-456
-
Guha S, Maheshwari SC (1964) In vitro production of embryos from anthers of Datura. Nature 204: 497
-
Guha S, Maheshwari SC (1966) Cell division and differentiation of embryos in the pollen grains of Datura. Nature 212: 97 ?98.
-
Hause B, Hause G, Pechan P, van Lammeren AAM (1993) Cytoskeletal changes and induction of embryogenesis in microspore and pollen cultures of Brassica napus L. Cell Biol Intl 17: 153 ?168
-
Hause B, van Veenendaal WLH, Hause G, van Lammeren AAM (1994) Expression of polarity during early development of microspore-derived and zygotic embryos of Brassica napus L. cv. Topas. Bot Acta 107: 369 ?472
-
Iwanowska A, Kieft H, van Lammeren A.A.M. (1998) Morphological and cytological changes in microspore-derived embryos of Brassica napus L. cv. Topas cultured in the presence of TIBA. Bull Polish Acad Sci Biol Sci 45: 187 ?194
-
Jain SM, Sopory SK, Veilleux RE (eds) (1996) In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers. Dordrecht
-
Jensen, CJ (1997) Monoploid production by chromosome elimination. In: Reinert J, Bajaj YPS (eds) Applied and Fundamental Aspects of Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 229 ?340
-
Jing, H-C, van Lammeren AAM, de Castro RD, Groot SPC, Hilhorst HWM, Bino RJ.
(1999) b-Tubulin accumulation and DNA synthesis are sequentially resumed in embryo organs of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seeds during imbibition.
Protoplasma 208: 230-239
-
Johri BM (1982) (ed) Experimental Embryology of Vascular Plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York
-
Lacadena J-R (1974) Spontaneous and induced parthenogenesis and androgenesis. In: Kasha KJ (ed) Haploid Plants: Advances and Potential. University of Guelph, Guelph, pp 13-32
-
Lichter R (1981) Anther culture of Brassica napus in a liquid culture medium. Z Pflanzenphysiol Bd 103: 229 ?237
-
Lichter R (1982) Induction of haploid plants from isolated pollen of Brassica napus. Z Pflanzenphysiol Bd 105: 427 ?434
-
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473-479
-
Sangwan RS, Sangwan-Norreel BS (1990) Anther and pollen culture. In: Bhoojwani SS (ed.) Development in Crop Science. 19: Plant tissue culture: applications and limitations. Elsevier, Amsterdam Oxford New York Tokyo, pp 220 ?241
-
Spurr AR (1969): A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26: 31-43
-
Straatman KR, Schel JHN (1997) Nuclear changes during pollen development and microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus. Bull Polish Acad Sci Biol Sci 45: 195 ?207
-
Sun M, Kieft H, van Lammeren AAM (1998) Cotyledon-derived diploid and haploid protoplast culture and diploid plant regeneration in Brassica napus cv. “Topas? Can J Bot 76: 530 ?541
-
Thorpe TA (ed) In Vitro Embryogenesis in Plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
-
Yang H, Zhou C (1982) In vitro induction of haploid plants from unpollinated ovaries and ovules. Theor Appl Genet 63: 97 ?104
-
Zao J, Simmonds DH (1995) Application of trifuralin to embryogenic microspore cultures to generate doubled haploid plants of Brassica napus. Physiol Plantarum 95: 304-309
-
Zhao J, Simmonds DH, Newcomb W (1996) High frequency production of doubled haploid plants of Brassica napus cv. Topas derived from colchicine-induced microspore embryogenesis without heat shock. Plant cell Reports 15:668-671
Return to R&D
IRIT-ARI Publications
|
|
